Chikiala Fm
Type Locality and Naming
Pranhita-Godavari Basin: King (1881) used the name for the sandstone unconformably overlying the Kota Fm near the village Chikiala, Maharashtra as the Chikiala Sandstone. The type area is the scarp of the hillock near Chikiala. [Original Publication: King, W. 1881. The geology of the Pranhita-Godavari valley. Mem. Geol. Surv, Ind., 18(30), 150-311]
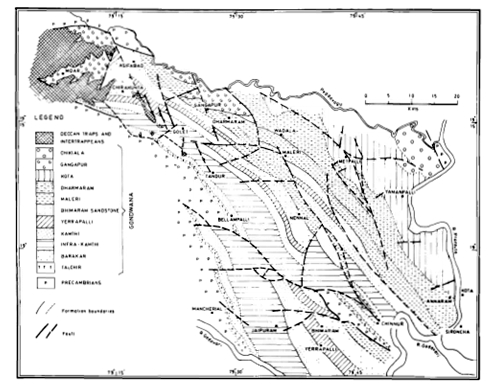
[Figure 1: Geological map of the northern Pranhita-Godavari valley between Pedda Vagu and Godavari River displaying the geographic extent of the Chikiala Formation (after Kutty et al., 1987)]
Lithology and Thickness
Sandstone. The formation comprises light brown, red, yellow and buff ferruginous sandstone and conglomerate. The rocks are highly ferruginous and local source for iron. A few clay bands are also present. The Chikiala Formation is about 275 m thick (Lakshminarayana, 1996).
Relationships and Distribution
Lower contact
Gangapur Fm unconformably overlying the Kota Fm in the western part of the Pranhita-Godavari Basin has been equated with the Chikiala Fm (Shah et al., 1970). But according to Raiverman (1986) Chikiala Formation overlies the Gangapur Fm, whereas Sastry et al. (1977) believe that the Chikiala Formation underlies the Gangapur Fm.
Upper contact
The sequence is covered by Deccan Traps Fm.
Regional extent
Pranhita-Godavari Basin: It forms the eastern margin of the Gondwana outcrops of the Pranhita-Godavari Valley.
GeoJSON
Fossils
Flora: Cladophlebis indica, Hausmannia cf. buchii, Hausmannia sp., Dictyozamites
sp., Nilssonia sp., Taeniopteris spathulata, Ha usmannia sp., Thinnfeldia odontopteroides, Otozamites sp. and Ptilophyllum acutifolium (Rao and Shah, 1959; Sastry et al., 1977).
Age
Depositional setting
The Chikiala Formation is interpreted as the deposit of an alluvial fan complex that exhibits northwesterly paleo-drainage.
Additional Information
References
Lakshminarayana, G. 1996. Stratigraphy and structural framework of the Gondwana sediments in the Pranhita–Godavari Valley, Andhra Pradesh. Gondwana Nine (1), Geol. Surv. India: 311–330. Sastry et al. 1977; Shah et al., 1970; Raiverman (1986); Rao, C. N., Shah, S. C. 1959. Fossil insects from the Gondwanas of India. Ind. Min., 12(1). 3.